Additive Manufacturing/ 3D Printing Using Composites
Additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, has revolutionized composite production by enabling the layer-by-layer construction of intricate composite structures. In the realm of composites, additive manufacturing techniques allow for the creation of complex geometries with precise fiber orientations and resin distribution, optimizing material performance. This technology offers the flexibility to customize parts, reduce waste, and experiment with novel composite combinations. By depositing materials layer upon layer, additive manufacturing facilitates the production of lightweight, high-strength components tailored for specific applications in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and healthcare, pushing the boundaries of what's achievable in composite design and fabrication.

ESSENTIAL READING
VIEW ALLAvoiding pitfalls in the design of LFAM composite components
Recoat temperature, part orientation and bead geometry are some key design variables to consider for a successful and reliable large-format additive manufacturing (LFAM) process.
Read MoreMaterials & Processes: Fabrication methods
There are numerous methods for fabricating composite components. Selection of a method for a particular part, therefore, will depend on the materials, the part design and end-use or application. Here's a guide to selection.
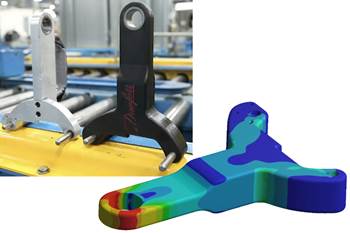
Read MoreHow to validate 3D-printed composite part performance
Integrated Computational Materials Engineering (ICME) workflow simulates composite material performance to speed development, optimize performance and reduce costs for a redesigned 3D-printed CFRP bracket.
Read MoreContactless measurement of temperature, pressure in composites
Magnetic microwires enable contactless measurement of temperature and pressure during cure and in service.
WatchKnowledge Centers

Explore the cutting-edge composites industry, as experts delve into the materials, tooling, and manufacturing hurdles of meeting the demands of the promising advanced air mobility (AAM) market. Join us at CW Tech Days to unlock the future of efficient composites fabrication operations.
LEARN MORE
Review the state of the art in design, simulation, failure analysis, digital twins, virtual testing and virtual inspection.
LEARN MORELatest Additive Manufacturing News And Updates
Generative Orthoses project to reshape orthopedic care
CRP Technology, MHOX and Istituto Ortopedico Rizzoli, one of the winners of the WORTH Partnership Project II, have developed bespoke orthoses using generative design, Windform GT fiberglass materials and PBF.
Read MoreAimen contributes to OVERLEAF 3D printed cryogenic tank
Dual thermoplastic composite system, developed to withstand temperatures below -250°C, demonstrates aviation decarbonization strategies.
Read MoreRoyal3D uses large-scale 3D printing for aquatic drone production
ShearWater aquatic drone, manufactured with fiberglass-reinforced recycled PETG, demonstrates precision 3D printing capabilities, sustainability focus and design innovation for maritime and heavy-duty applications.
Read MoreHaddy opens LFAM microfactory in Florida for localized, agile composite parts production
CEAD helped Haddy inaugurate the AI-powered microfactory complete with eight Flexbot robotic systems for end-to-end 3D printing and 16-times production capacity.
Read MoreRAW Idea expands composites capabilities with hybrid 3D printer
Installation of LSAM printer from CEAD broadens RAW Idea’s ability to work with advanced composites and manufacture parts with greater efficiency and precision.
Read MoreAirtech acquires Kimya assets, extends AM filament capabilities
Kimya’s filaments portfolio will be offered alongside Airtech’s Dahltram pellet and filament resins, adding to its LFAM and thermoplastic product line.
Read MoreFeatured Posts
JEC World 2025 highlights: New thermoplastics, PI fiber, solutions for FR, machining, digitized processes and more
CW senior technical editor Ginger Gardiner discusses latest developments in composites from this year’s show.
WatchVIDEO: Enhancing composite tooling with additive manufacturing
At JEC World 2025, CW editor-in-chief Scott Francis explored the latest advancements in composite tooling with Massivit and Sika.
WatchFIDAMC expands composites R&D into new markets and advanced manufacturing centers
Pioneering technocenter advances RTM, thermoplastic composites, additive manufacturing, microwire, novel lighter weight LSP and more.
Read MorePost Cure: Tool-less direct extrusion enables efficient, complex composite structure development
Backed by AI software, Hans Weber’s large-format 3D printing capabilities resulted in the successful development of a Savonius wind turbine blade in under two hours.
Read MoreLarge-format AM speeds plug production for manufacture of composite boat molds
Hungarian manufacturer Rapid Prototyping transitioned its conventional foam milling process to 3D printing to produce faster, higher quality, recyclable foam plugs and composite boat molds.
WatchPost Cure: Continuous fiber injection reinforces 3D printed parts
Reinforce 3D’s postprocessing technology injects continuous carbon fibers and liquid resin into parts with tubular cavities, enabling reinforcement and integral joining for components like a satellite antenna support.
Read MoreFAQ: Additive Manufacturing
What is additive manufacturing in composites?
Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, in composites involves the layer-by-layer deposition of composite materials, such as continuous fibers or chopped fibers within a matrix, to create complex parts or structures.
What types of additive manufacturing methods are used for composites?
Various methods are employed, including Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF), Continuous Fiber 3D Printing (CFF), Binder Jetting, Directed Energy Deposition (DED), and others that selectively deposit materials to build composite parts.
What composite materials can be used in additive manufacturing?
Additive manufacturing processes can work with a range of composite materials, such as carbon fiber-reinforced polymers (CFRPs), glass fiber composites, and even advanced materials like nanocomposites or hybrid composites.
What are the advantages of additive manufacturing in composites?
Benefits include the ability to create complex geometries, lightweight structures, reduced material waste, customization, rapid prototyping, and the integration of functional features within parts.
Are there limitations to additive manufacturing in composites?
Challenges include limitations in scaling for large-scale production, post-processing requirements, ensuring consistent mechanical properties, and the need for advancements in material options.